
VTY (Virtual Teletype) Telnet access refers to a method of remote access to a network device, such as a router or switch, through the Telnet protocol using virtual terminal lines. This method is widely used in network management.
Let’s break down these concepts for a comprehensive understanding:
Virtual Teletype (VTY): VTY is a virtual port on a network device that enables remote access. Unlike physical ports on a router or switch, VTY lines are not associated with physical interfaces. Instead, they are virtual lines through which users can establish remote connections to the device.
A device typically supports multiple VTY lines, allowing several simultaneous remote connections.
Telnet Protocol: Telnet is a network protocol that allows for a two-way interactive text-oriented communication facility using a virtual terminal connection.
It’s one of the oldest protocols used for remote access and operates on the client-server principle. The Telnet client initiates a connection to a Telnet server (in this case, the network device) to perform remote operations.
VTY Telnet Access in Network Devices: In routers and switches, VTY Telnet access is configured to allow network administrators to manage the device remotely. By connecting to a VTY line via Telnet, administrators can execute configuration commands, modify settings, and troubleshoot issues without needing physical access to the device.

Security Aspects: While VTY Telnet access is convenient, it has significant security drawbacks. The Telnet protocol transmits data, including login credentials, in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception and eavesdropping. In modern networks, it’s often recommended to use Secure Shell (SSH) instead of Telnet for secure encrypted connections. SSH provides similar functionality to Telnet but with enhanced security features.
Configuration: Configuring VTY Telnet access on a network device involves setting up VTY lines, specifying which IP addresses are allowed to connect, and setting password protection. The configuration ensures that only authorized users can access the device remotely.
How to Control VTY Telnet Access Explained with Example.
Active interfaces on a network router can be accessed by users on the network if not properly secured. Users or Hackers might try telnetting the network router through the VTY access.
To stop this from happening, the best practice is for you to use a standard IP access list to limit telnet access to every network or IP address on the router. Applying a standard IP access list to the VTY lines eliminates the option of using telnet protocols and destination addresses since it does not matter which interface address a user or hacker is using as a target for the telnetting session.
Using a standard IP access list to restrict VTY access enables you to define which IP addresses are allowed telnet access to the router EXEC process. You can control which workstation or network accesses your router with an ACL and an access-class statement to your VTY lines
You can also use extended access lists; don’t get me wrong, but that means you have to apply it inbound on every interface, imagine doing this on a large network with dozens if not hundreds of interfaces!
We use the network topology below as an example:
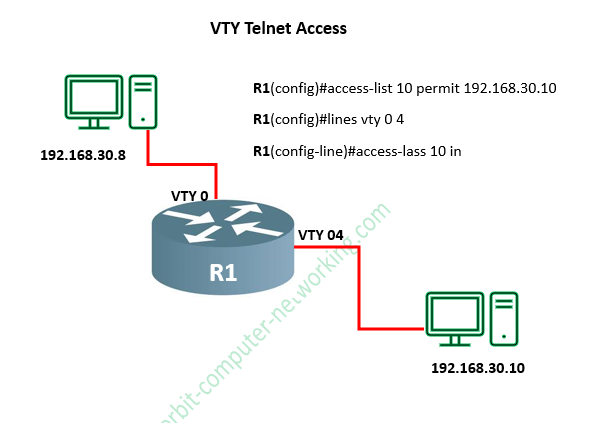
Below, we are going to create a standard IP access list that permits only a host 192.168.30.10 (or hosts) to be able to telnet to the router R1, the command and configuration look like this:
R1#config t
R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 192.168.30.10
R1(config)#lines vty 0 4
R1(config-line)#access-lass 10 in
The above configuration simply means that only the IP address 192.168.30.10 or host is allowed to Telnet or access the R1 router.
Access List Configuration Example Extended ACLs Explained IPv6 ACLs
Applying Extended ACLs on Interfaces Complex ACLs How to Configure Switchport ACLs
Numbering and Naming ACLs
Time Base ACLs

